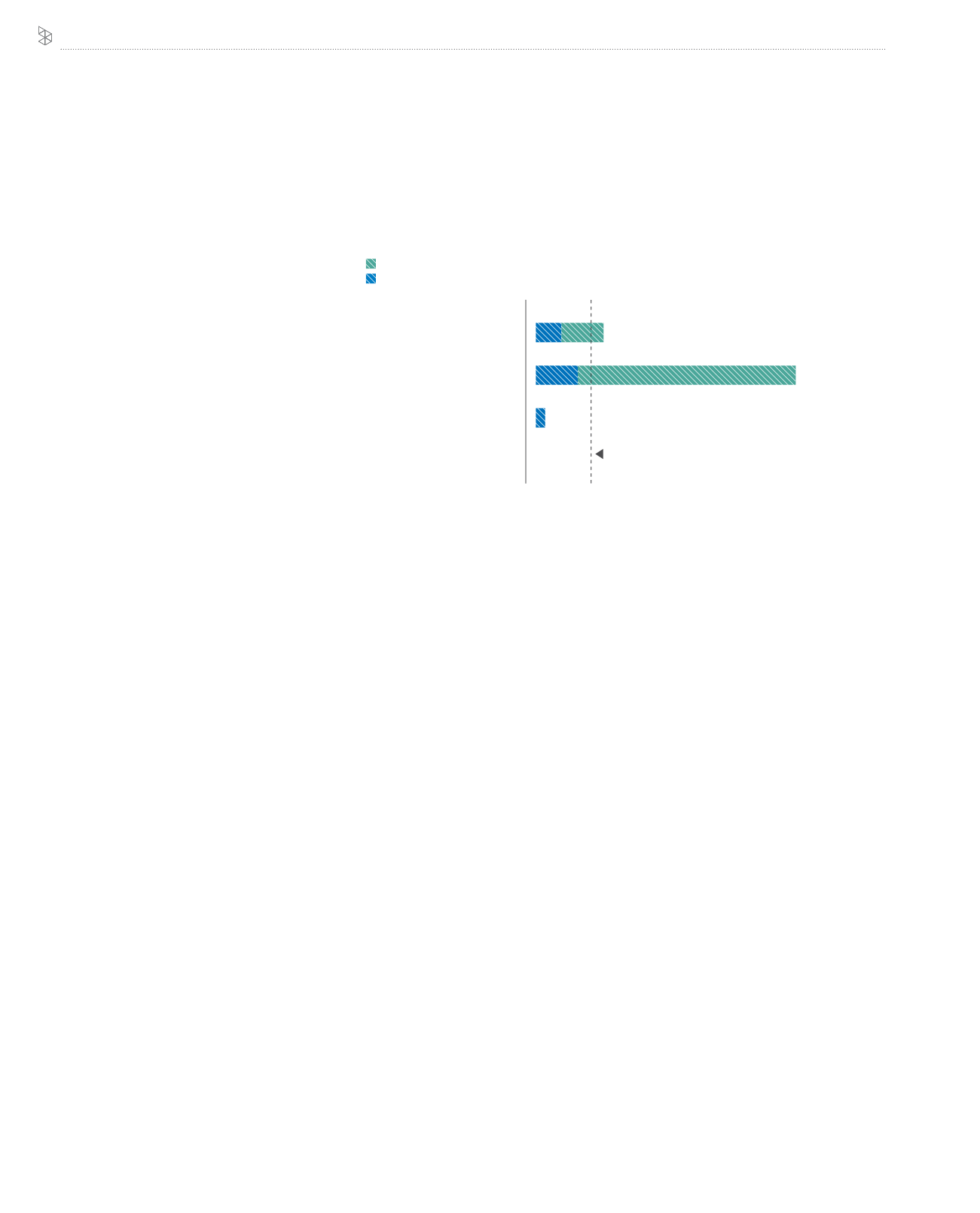
NATIONAL CONTRIBUTION REPORT
68
Axiata Group Berhad | Sustainability & National Contribution Report 2016
- Partnerships with Anchor Partners
including Government regulatory
agencies to fund Bumiputera SME
and SMI companies, as well as
funding through Axiata Digital
Innovation Fund (ADIF)
(ii)
Developing Employees
- Trained 127 employees under the
Celcom Accelerated Development
Programme
- Hired 622 Skim Latihan 1Malaysia
(SL1M) trainees to provide fresh
graduates with practical working
experience
- Conducted an entrepreneurship
training programme with the
Ministry of Higher Education
(MoHE) in 2016 to develop student
entrepreneurial abilities
(iii)
Contributing to Society
- Contributed RM8 million to the
Badminton Association of Malaysia
(BAM) to develop the sport
Supporting our Local Business Partners
and SMEs
At the Group level, Axiata established ADIF,
to fund and develop local digital businesses.
ADIF has also been directed to ensure
that 50% of its investees are Bumiputera
majority-owned businesses. By end 2016,
ADIF has invested RM23 million in 12
companies.
At the OpCo level, Celcom supports
local industry development through its
Local Partner Development Programme
(LPDP) and its Vendor Development
Programme (VDP). The LPDP is focused
on developing Bumiputera vendors while
the VDP expands its scope to include all
Malaysian vendors. These programmes are
designed to help vendors become more
competitive by providing guidance and
creating networking opportunities in the
industry. Celcom also runs development
programmes for its business and strategic
partners through its Business Development
Programme (BDP) and Strategic Partners
Development Programme (SDP).
SMEs – the engine of the Malaysian
economy
SMEs contributed 36% of Malaysia’s total
GDP in 2014, and this is expected to reach
41% by 2020. However, many SMEs have
yet to take advantage of e-commerce to
grow their business.
The National eCommerce Strategic
Roadmap seeks to increase e-commerce
penetration among SMEs to improve their
productivity and ability to compete with
domestic and international brick-and-
mortar stores. Specific goals include:
(i) Establishment of a one-stop eBusiness
resource for SMEs
(ii) Increased promotion and marketing
of e-commerce to SMEs.
The Roadmap estimates e-commerce to
account for 6% of SMEs’ total revenues by
2020 (see Figure 5).
Digitisation increases productivity and
competitiveness of SMEs
Only 20-25% of Malaysia’s SMEs have
adopted ICT in their business operations,
partly due to a lack of awareness of the
benefits of digital platforms. This hampers
their productivity and competitiveness,
Services - e.g. wholesale, retail,
financial services (581K)
6%
10%
2%
52%
15%
10%
Manufacturing (38K SMEs)
Agriculture (7K SMEs)
Construction, other (19K SMEs)
e-commerce share of SME revenue in
other developed countries
Figure 5: % e-commerce value from SMEs in Malaysia - by SME sector
US benchmark for e-commerce sector value contribution
% of e-commerce value from SMEs in Malaysia
Source: Jehangir et al., “Towards Digital Economy: The Development of ICT and E-Commerce in Malaysia”, 2011
and prevents SMEs from offering their
products to online consumers. As a result,
less than 10% of SMEs’ GDP contribution
is derived via e-commerce, although this
could rise with increased engagement
with ICT.
Dialog offers the best Tourist Mobile
Plans for tourists to get connected when
enjoying the beauty of this paradise island.
The Malaysia External Trade Development
Corporation uses ICT in its eTRADE
programme to help SMEs to reach out to
newbuyers in international e-marketplaces.
The programme includes training and
online assistance to participating SMEs,
and on-boarding them onto the e-
marketplace.
Expanding
Connectivity
to
Underserved Areas
The Malaysian Government implemented
its National Broadband Initiative in 2010 to
make high-speed internet accessible and
affordable to all Malaysians, with particular
emphasis on rural populations. Online
access has been viewed by the Government
as necessary for the social and economic
uplift of rural Malaysia, particularly in the
areas of commerce and education.
NATIONAL CONTRIBUTION
REPORT